ADITYA L1 Mission Know everything about ADITYA-L1 | Why is ADITYA-L1 Mission Important to India
Hi Readers,
As you will be aware that, Indian ISRO has launched another mission named Aditya L1 after successfully landing of Chandrayaan 3.
Aditya L1 Mission was launched by ISRO on September 2, 2023 11:30 AM. In this article we will conduct in-dept analysis about the objective of Aditya L1, Its importance and impact of Aditya L1 on human race.
Table of Contents
What is Aditya L1 ?
Aditya-L1 is a satellite with main objective to analyze and study Sun. This mission will greatly help to discover unknown facts about sun which are not currently discovered to human race.
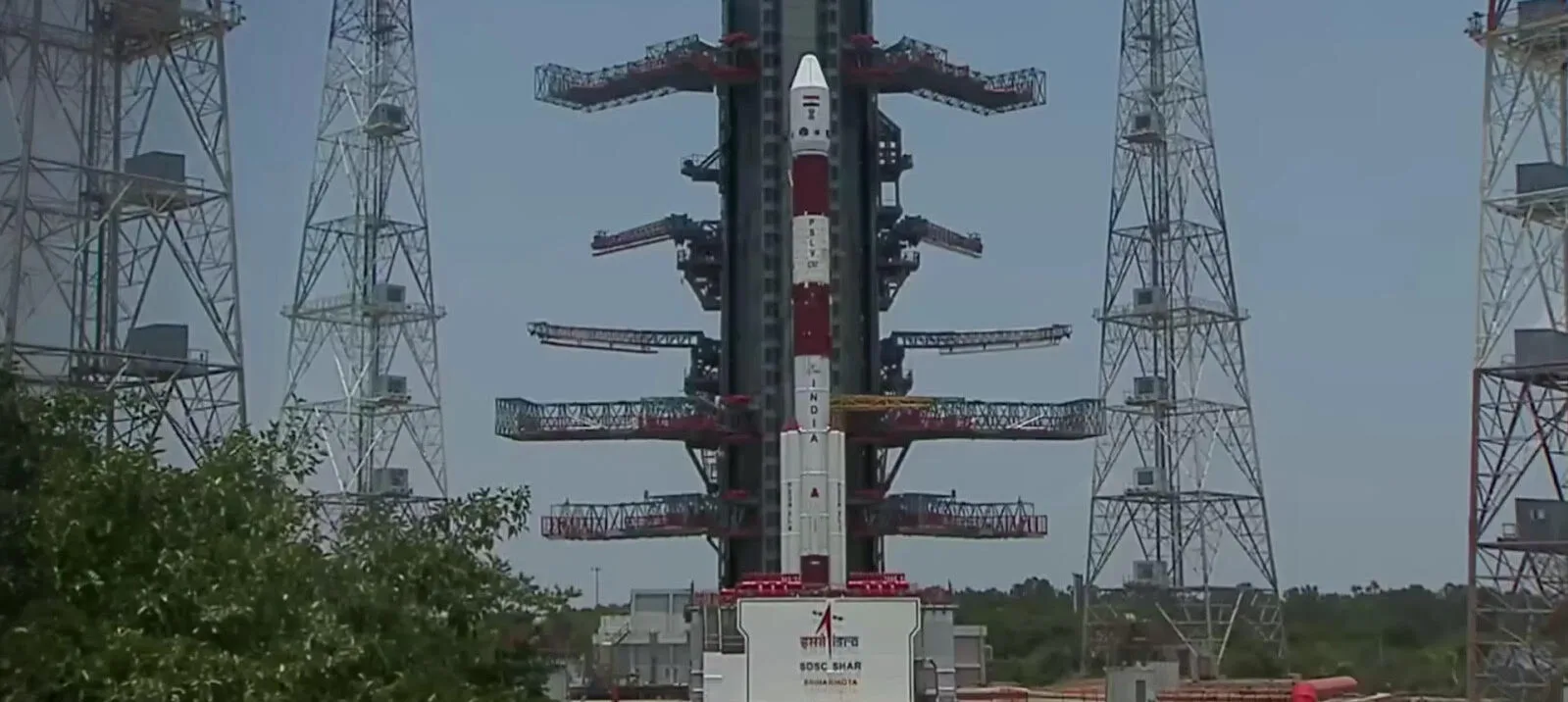
Aditya L1 was launched on September 2, 2023 11:30 AM from the Second Launch Pad (SLP) at Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
Objective of Aditya L1
As we know, the Sun is a giant sphere of gas and the objective of Aditya-L1 will be to study the outer atmosphere of the Sun. Aditya-L1 will neither land on the Sun nor approach the Sun any closer. The spacecraft will be directed towards the Sun. Aditya-L1 will be placed in a halo orbit around the virtually marked point in space Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km or about 1% of the Earth-Sun distance from the Earth.
Aditya-L1 has 7 distinct payloads developed and all are developed indigenously. Five payloads are developed by ISRO and two payloads are designed by Indian academic institutes in collaboration with ISRO.
Aditya L1 Study
Below are the list of scientific studies performed during Aditya L1 mission, provided by ISRO Scientists,
- Study of the dynamics of the solar upper atmosphere (chromosphere and corona).
- Drivers of space weather (solar wind dynamics, composition, and origin)
- Study of coronal and chromospheric heating, plasma physics, the beginning of coronal mass ejections, and flares
- Determine the series of events that take place at various layers (chromosphere, base, and extended corona) and ultimately result in solar eruptive events.
- The heating mechanism of the solar corona and its physics.
- Temperature, velocity, and density measurements of the coronal and coronal loop plasma.
- Watch the in-situ particle and plasma environment that the Sun provides, since this information will be used to investigate particle dynamics.
- Coronal mass ejections (CMEs): evolution, behavior, and origin.
- Magnetic field measurements and field topologies in the solar corona.
What is Lagrange point 1 (L1) ?
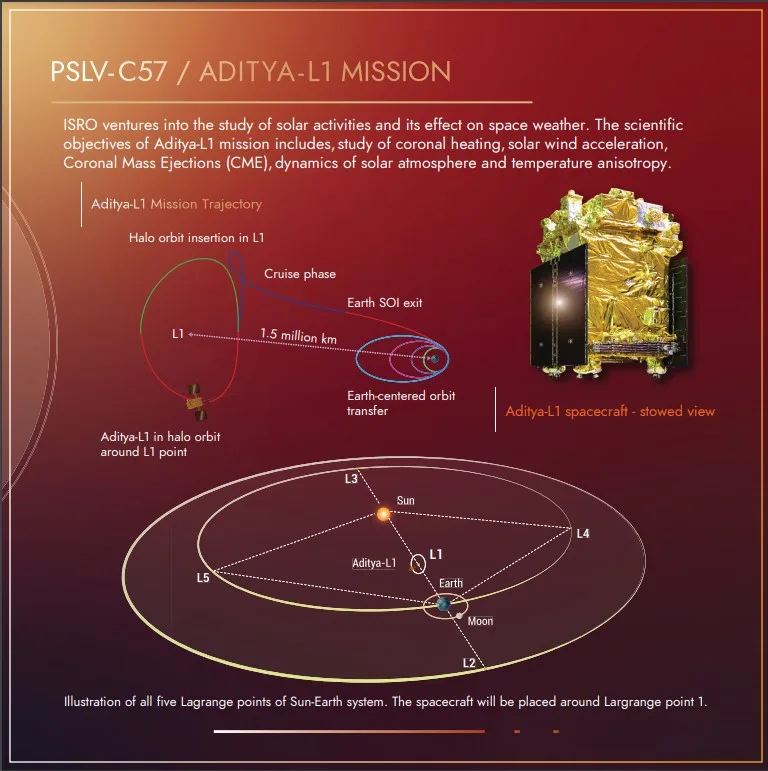
Aditya L1 will be launched from India and will stationed in virtually marked point in space Lagrange point 1 (L1). L1 is a location in outer space where the gravitational forces of two celestial bodies, the Sun and Earth in this case, are in equilibrium.
This means that an object, Aditya L1 satellite in this case, placed there will theoretically remain relatively more stable with respect to both Earth and Sun.
Is Lagrange point 1 (L1) important ?
Lagrange point 1 (L1) point is selected strategically for this mission post several studies and research by our scientists and holds a very important part of the mission. A major advantage of L1 is that, since the satellite will be placed at this point facing sun, Aditya L1 will have the view of the Sun continuously without any intervention, this means any disturbance such as an eclipses will not cause any problem to the mission.
Lagrange point 1 (L1) will provide a great advantage and optimal condition for Aditya L1 to observe solar activities and it’s effect on space and weather in real time.
How will Aditya L1 study the Sun ?
Aditya-L1 is a dedicated satellite to perform comprehensive study of the Sun. It has seven distinct payloads which are all developed indigenously.
Five payloads are developed by ISRO and two payloads are designed by Indian academic institutes in collaboration with ISRO.
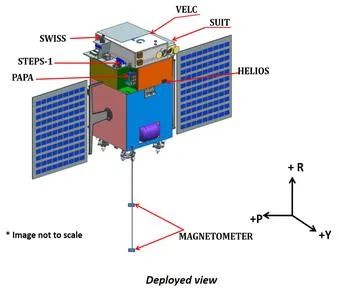
These payloads will help to observe the chromosphere, photosphere, and the outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic waves and magnetic field detectors. While four payloads will directly view the Sun, the remaining three payloads carry distinct scientific studies of the atmosphere, particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1.
These payloads will provide important contribution in scientific studies of the propagatory effect of solar dynamics in the interplanetary medium, which means it will help to study relating to travel between planets.
These payloads are also expected to provide human race with the most crucial information to understand the problem of coronal heating, coronal mass ejection, pre-flare and flare activities and their characteristics, propagation of particles and fields, dynamics of space weather and much more in-dept scientific studies.
What is Aditya L1 mission duration
The duration of Aditya L1 mission is expected to be for 5 Years 2 Months as planned. Aditya L1 will spend the whole mission lifespan orbiting around L1 holo space in an irregularly shaped orbit.
This route will be perpendicular to the line joining the Earth and Sun.
How to watch of Aditya L1 mission launch
For the one who are interested, they can watch videos regarding the launch of Aidtya L1 on ISRO website, Facebook, YouTube
Related Articles
Russia’s Luna-25 has crashed into the moon – Click Here
Chandrayaan 3 Everything you need to know – Click Here
Latest list of ISRO’s next Missions – Click Here
FAQ
What is the full form of ISRO ?
ISRO Stands for Indian Space Research Organisation
Who is considered as the “founding father” of Indian Space Programme?
Dr Vikram A Sarabhai is considered as the founding father of space programmes in India.
When was ISRO formed?
ISRO was formed on August 15, 1969.
When was Department of Space constituted?
Department of Space (DOS) and the Space Commission were set up in 1972. ISRO was brought under DOS on June 1, 1972
What is the main objective of ISRO?
The prime objective of ISRO is to develop space technology and its application to various national needs.
How these Objectives are met?
ISRO has established two major space systems, INSAT for communication, television broadcasting and meteorological services, and Indian Remote Sensing Satellites (IRS) system for resources monitoring and management. ISRO has developed two satellite launch vehicles, PSLV and GSLV, to place INSAT and IRS satellites in the required orbits.
Where the Satellites are made?
Satellites are made at U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), Bangalore
Where the Rockets / Launch vehicles are made?
Rockets / Launch Vehicles are made at Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram
From where are the rockets launched?
ISRO’s Launch facility is located at SDSC SHAR from where Launch Vehicles and Sounding Rockets are launched. Sounding rockets are also launched from TERLS at Thiruvananthapuram
How can I order for Satellite data?
You can get data from National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), Hyderabad. Visit the website: www.nrsc.gov.in for more details
Where the Space Programme began in India?
Indian Space Programme began at Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) located at Thumba near Thiruvananthapuram
When did India begin developing its own rockets?
India’s first indigenous sounding rocket, RH-75, was launched on November 20, 1967
Source –
Image Source – By Indian Space Research Organisation – Original publication: Click Here
source: Click Here
Fair use Click here
By Indian Space Research Organisation (GODL-India), GODL-India, Link